The AI Function in Google Sheets brings the power of Gemini AI directly into your cells.
It uses Gemini’s large language models (LLMs) to process the text prompts and return helpful responses. It’s akin to using a prompt in the chat window of Gemini, but with the convenience of being accessible in your Sheet.
And it’s as easy to use as any other formula!
Who has access to the AI Function?
The AI Function is available to people on the following Google Workspace plans:
- Business Standard and Plus
- Enterprise Standard and Plus
- Customers with the Gemini Education or Gemini Education Premium add-on
- Google AI Pro and Ultra
Anyone who previously purchased these legacy add-ons will also have access to the AI function:
- Gemini Business
- Gemini Enterprise
Additionally, it’s available to users enrolled in the Google Workspace Labs program.
☠️ Note: If you don’t have access to the function, you can achieve any of these results by copy-pasting data into Gemini (or ChatGPT or Claude) and running the prompt there. And then you can paste the results back into your Sheet. Obviously, it’s not as convenient!
How to use the AI Function
The AI function is simple to use and has the following form:
=AI( "prompt" , [optional range] )
It takes two arguments:
- the prompt, which is a description of the action you want the function to perform, enclosed in double quotes, and
- an optional range, which is a reference to a single cell or range containing information that provides extra context to the AI function.
The AI function is most useful for working with text. There are four broad actions that it can perform:
- Sentiment analysis
- Summarizing text
- Categorizing text
- Generating text
Example 1: Sentiment Analysis with the AI Function
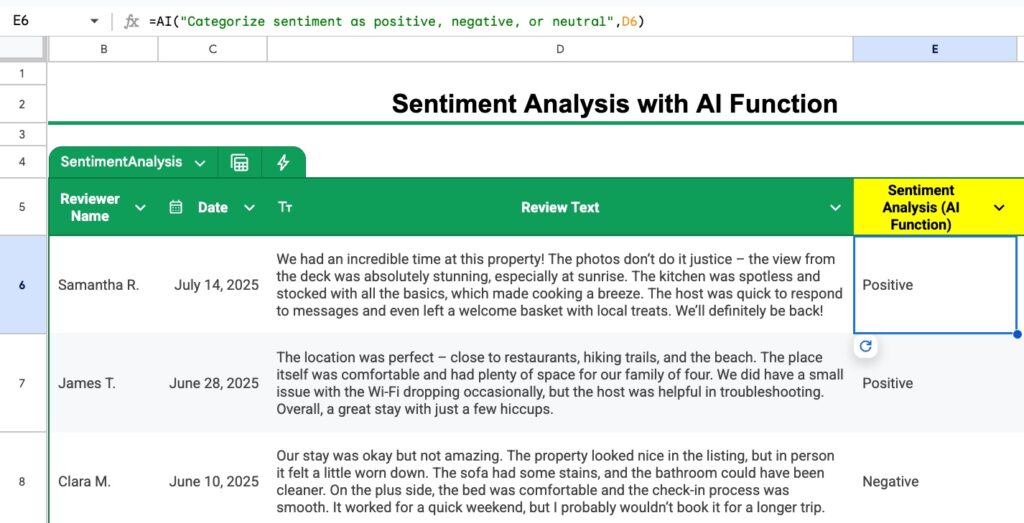
Suppose you manage an AirBnb and you have a Google Sheet containing reviews. You can use the AI function to analyze the sentiment of these reviews to identify positive and negative reviews.
Use this prompt:
Categorize sentiment as positive, negative, or neutral
inside the AI function as follows:
=AI( "Categorize sentiment as positive, negative, or neutral" , D6 )
where the cell D6 contains the review.
Alternatively, we can include the reference to cell D6 directly in the prompt argument by concatenation:
=AI( "Categorize sentiment of the review in " & D6 & "as positive, negative, or neutral" )
In this case, we don’t specify the option range argument.
Perhaps the only benefit of this second approach is that it lets you reference non-contiguous ranges, i.e. multiple cells in different parts of your Sheet.
For example, this text generation AI formula references cells in column B and D (i.e. non-adjacent), which wouldn’t be possible with a single range argument:
But if you are using a single cell or range, it’s easier to include it as the second argument of the AI function.
Example 2: Sentiment Analysis as a Rating Chip
An alternative way to show sentiment analysis is to ask the AI function to output a rating between 1 and 5 and then format the cells as Rating chips.
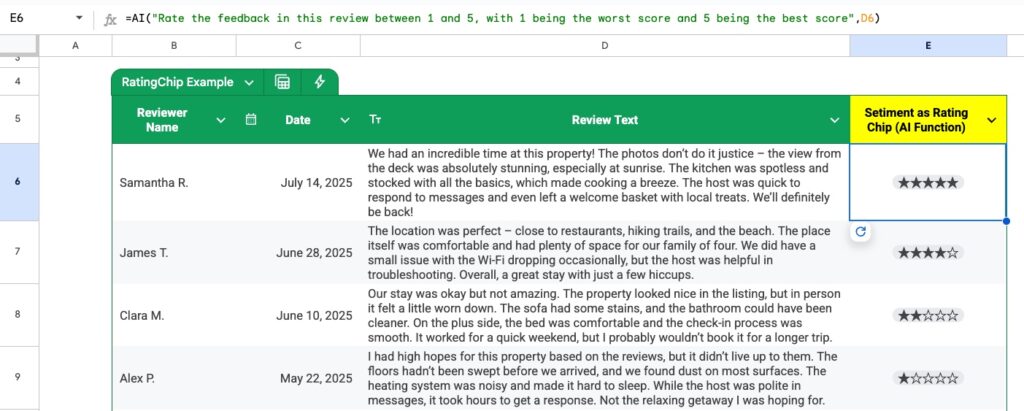
The AI formula is:
=AI( "Rate the feedback in this review between 1 and 5, with 1 being the worst score and 5 being the best score" , D6 )
This gives an output between 1 and 5 (technically, 0 to 5 would also work).
Then highlight the cells with the rating numbers and change them to Rating chips via the menu:
Insert > Smart chips > Rating
Alternatively, if your data is in a Table, you can change the column type to a Rating chip under the column menu:
Edit column type > Smart chips > Rating
Example 3: Summarize Text
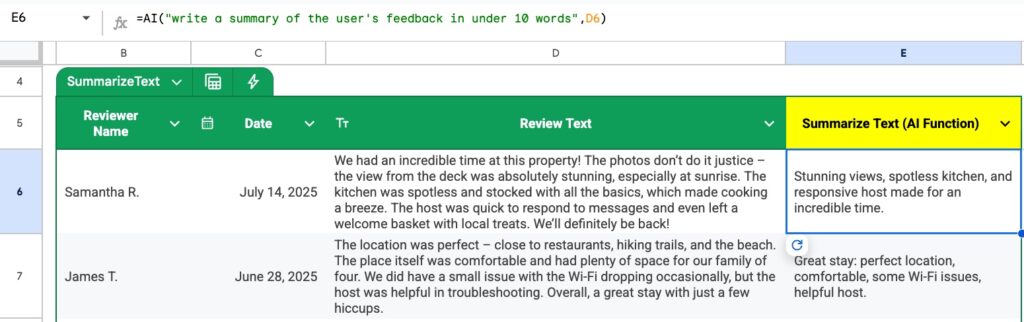
With the review text in cell D6, we can use this formula to summarize the text:
=AI( "write a summary of the user's feedback in under 10 words" , D6 )
Example 4: Categorize Text
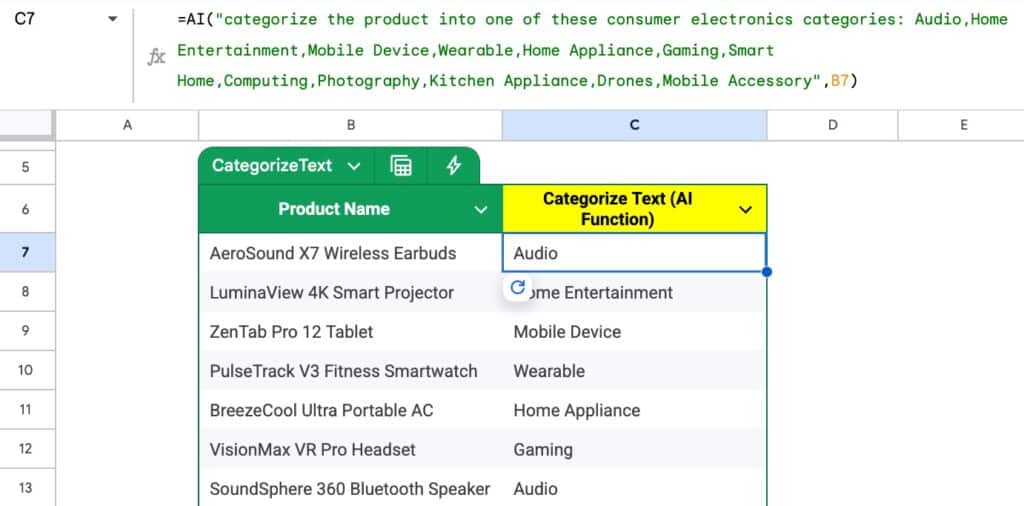
Suppose we have a list of products that we need to categorize into groups. It’s a hugely time consuming task.
The AI function can dramatically speed that process up.
With the data in column B, we can use a formula like this to categorize the products:
=AI( "categorize the product into one of these consumer electronics categories: Audio,Home Entertainment,Mobile Device,Wearable,Home Appliance,Gaming,Smart Home,Computing,Photography,Kitchen Appliance,Drones,Mobile Accessory" , B7 )
Example 5: Generate Text
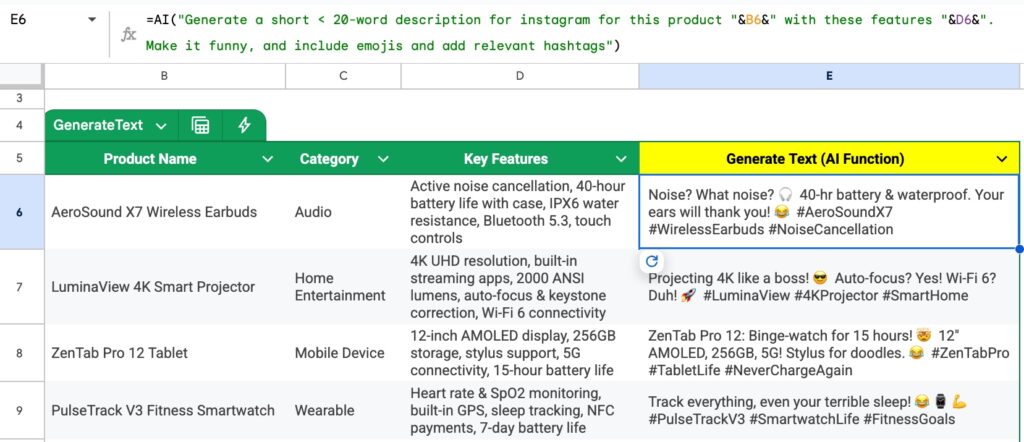
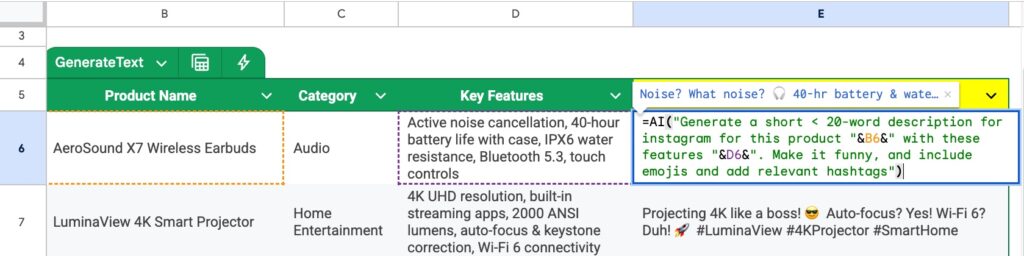
In this example, we use the AI formula to generate marketing copy for products on Instagram. We tell Gemini to add emojis and hashtags in the output.
Note also that because the product name is in column B and the key features are in column D, we need to insert the references into the prompt:
=AI( "Generate a short less than 20-word description for instagram for this product " & B6 & " with these features " & D6 & ". Make it funny, and include emojis and add relevant hashtags" )
This just inserts the value from cells B6 and D6 into the text string prompt before the AI formula runs it.
Example 6: Generate Email Drafts
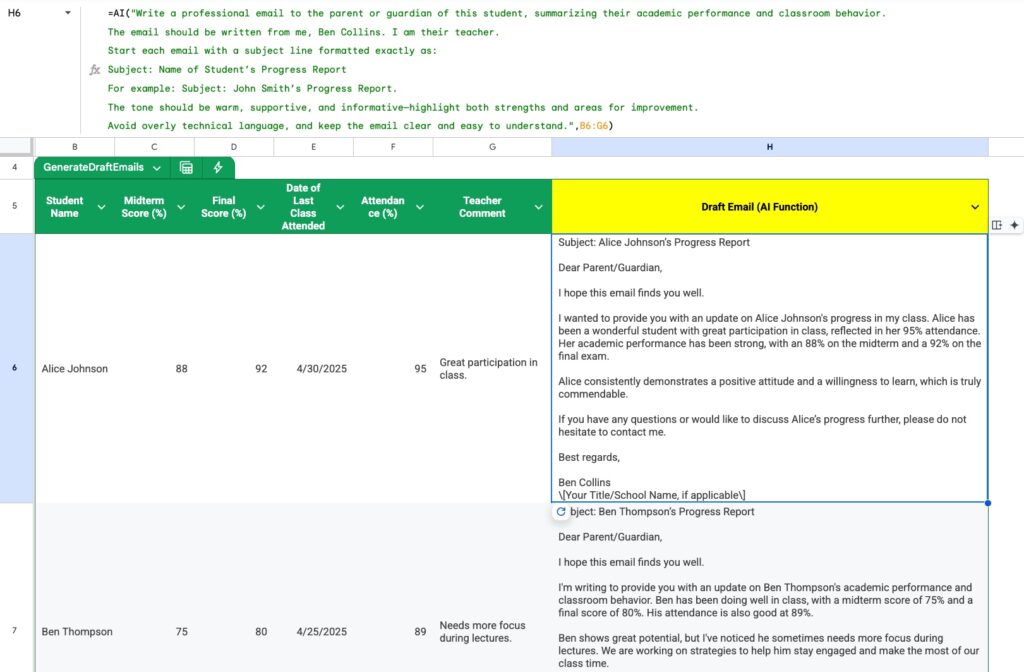
We use a longer, ultra-specific prompt to ensure the emails are formatted exactly as we want them.
And the formula references data in the range B6 to G6 (i.e. the whole Table row) for context:
=AI( "Write a professional email to the parent or guardian of this student, summarizing their academic performance and classroom behavior.
The email should be written from me, Ben Collins. I am their teacher.
Start each email with a subject line formatted exactly as:
Subject: Name of Student’s Progress Repor
For example: Subject: John Smith’s Progress Report.
The tone should be warm, supportive, and informative—highlight both strengths and areas for improvement.
Avoid overly technical language, and keep the email clear and easy to understand.",B6:G6)
This is part of a YouTube tutorial on turning Google Sheets data into Gmail drafts, with the AI Function and Apps Script.
Example 7: Explaining Formulas
At the time of writing (August 2025), the AI function cannot be nested inside other functions, or vice versa.
To combine it with other functions, we have to create helper columns that output intermediate steps.
So before we can explain that complex formula in cell A1, we have to use the FORMULATEXT function to turn it into text:
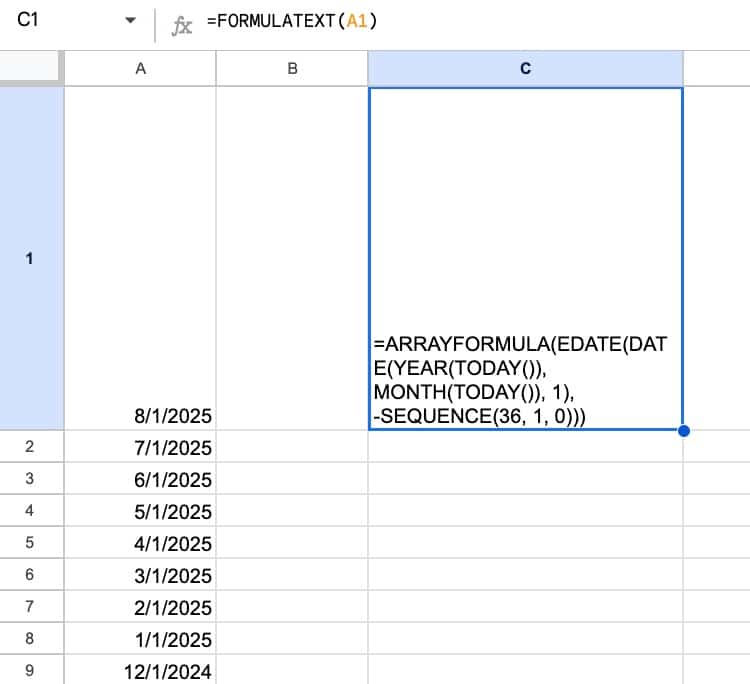
The formula is:
=FORMULATEXT(A1)
Then we can use the AI function to explain that text version of the formula:
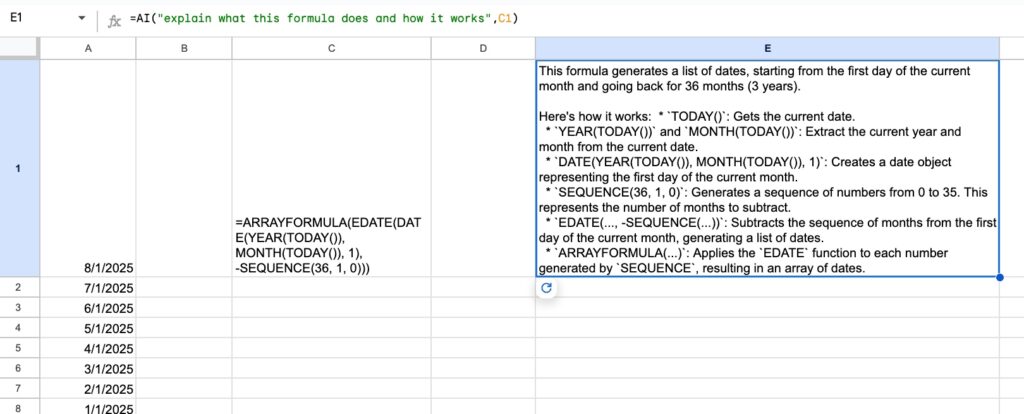
The AI formula is:
=AI("explain what this formula does and how it works",C1)
Example 8: Categorize Stock Tickers
We can use the AI function to categorize stock tickers into industry categories:
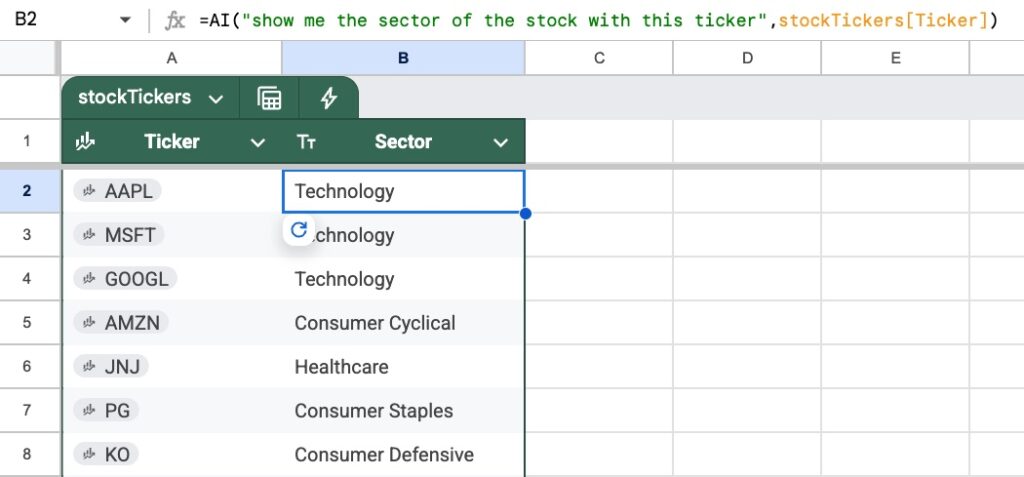
The formula is:
=AI("show me the sector of the stock with this ticker", stockTickers[Ticker])
where the stock tickers are in a Table called “stockTickers”.
Example 9: Parse Addresses to Extract Data
The AI function is a huge help at parsing messy addresses and extracting the component parts:
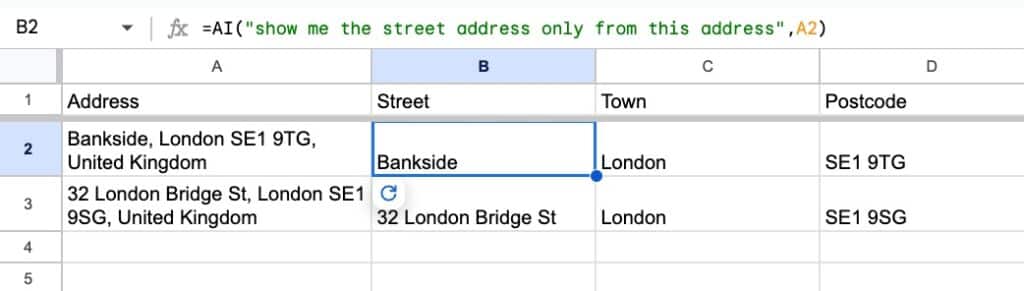
The formulas for these columns are:
=AI("show me the street address only from this address",A2)
=AI("show me the town only from this address",A2)
=AI("show me the postcode only from this address",A2)
Example 10: Unpivot Data
For a final example, here it is helping to UNPIVOT data, which is turning wide data into tall data format. It’s notoriously difficult to do with regular formulas.
However, if you can handle complex formulas, the old-school, deterministic method is still more convenient since we can’t nest the AI function inside other functions yet.
But for reference, here’s how we can create an AI formula to unpivot data.
First, we unpivot data with AI:
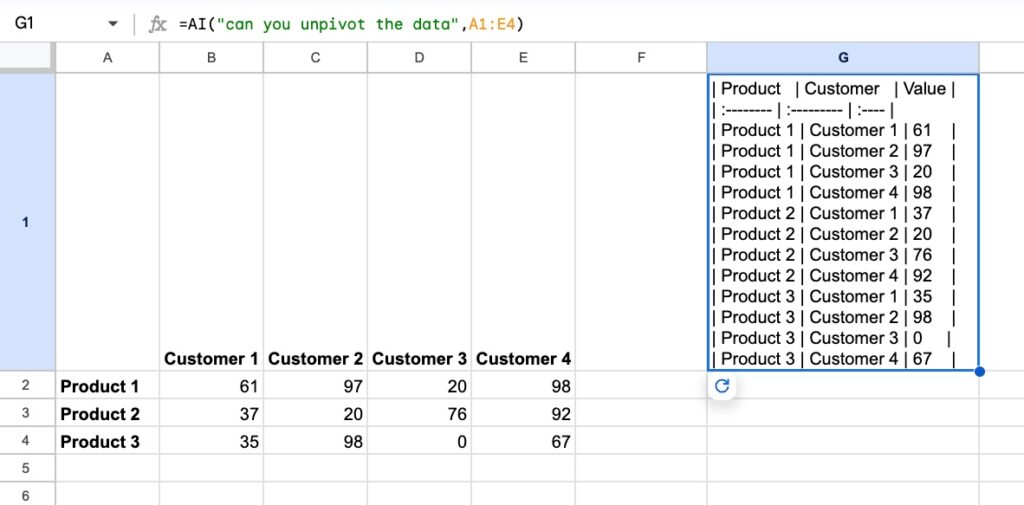
The formula is:
=AI("can you unpivot the data",A1:E4)
Then we use regular functions to parse into rows:
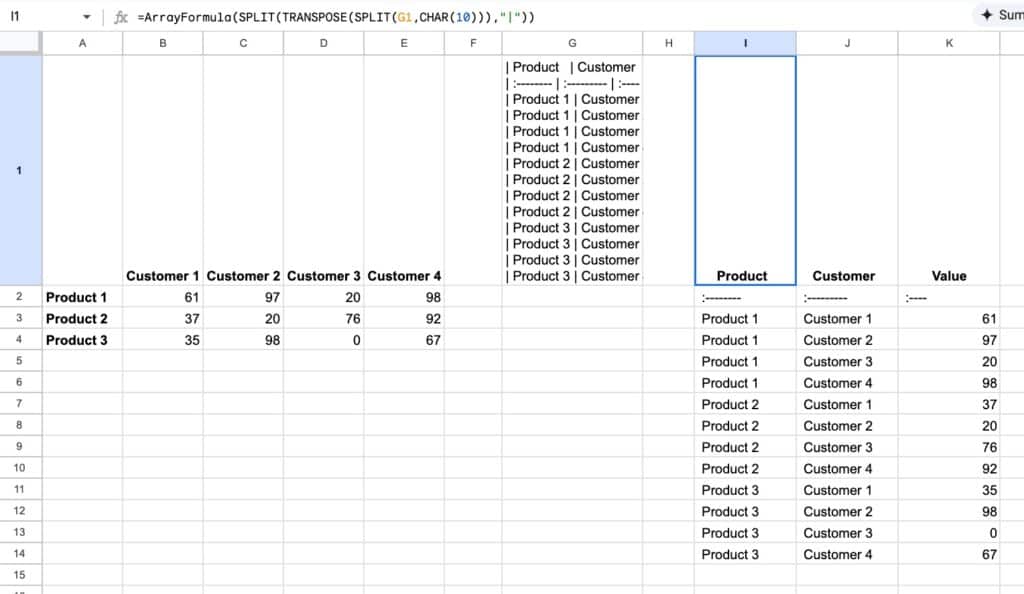
The formula is:
=ArrayFormula(SPLIT(TRANSPOSE(SPLIT(G1,CHAR(10))),"|"))
What the AI Function CANNOT do
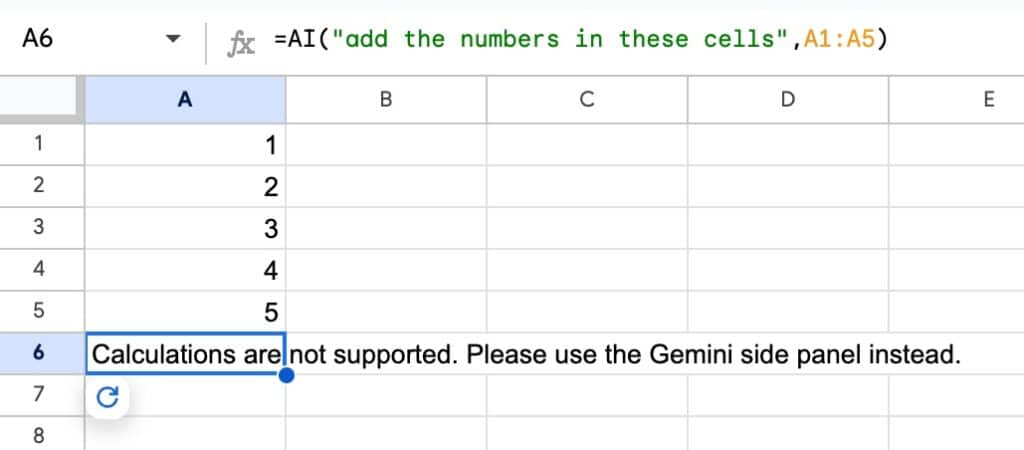
1) it cannot perform calculations like regular functions. If you try, you’ll get an error message:
With all the hype around AI at the moment, it’s tempting to apply it to everything we do.
So it’s good to step back and ask yourself if you really need an AI function. Most spreadsheets tasks that involve data will still be in the domain of regular, deterministic functions, like SUM, AVERAGE, FILTER, etc.
So don’t fall into the trap of trying to apply AI to everything!
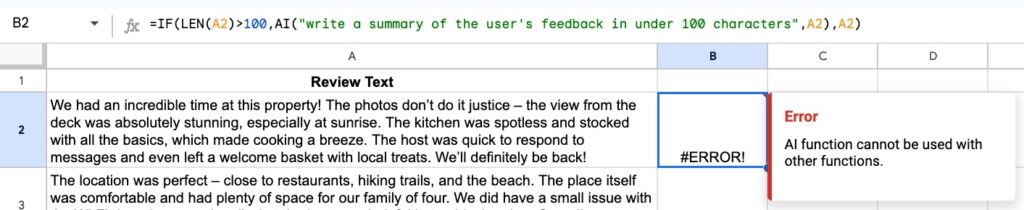
2) it cannot be nested inside other functions.
If you try to nest the AI function, for example inside an IF function as shown here, you’ll get an error message:
3) the AI function has limits to how much it can generate in a 24-hour window. If you hit the limit, you won’t be able to click the “Generate” button until 24 hours has passed.
4) if you select multiple cells with AI functions and click to generate outputs, only the first 200 cells will be generated. Once the first batch of 200 is complete, you can generate the next batch of 200 cells, and onwards.
5) if you access Sheets through other cloud storage providers (e.g. Dropbox, Box, etc.) then you can’t generate content with the AI function.
6) The AI function cannot generate other functions, pivot tables, or charts.
AI Function Template
Download the Complete Guide to the AI Function Template
Click on “Use Template” in the top right corner to make your own copy.
There is no Apps Script with this template.
Additional prompt examples in the Google documentation.