The Cantor set is a special set of numbers lying between 0 and 1, with some fascinating properties.
It’s created by removing the middle third of a line segment and repeating ad infinitum with the remaining segments, as shown in this gif of the first 7 iterations:
The formulas used to create the data for the Cantor set in Google Sheets are interesting, so it’s worth exploring for that reason alone, even if you’re not interested in the underlying mathematical concepts.
But let’s begin by understanding the set in more detail…
What Is The Cantor Set?

The Cantor set was discovered in 1874 by Henry John Stephen Smith and subsequently named after German mathematician Georg Cantor.
The construction shown in this post is called the Cantor ternary set, built by removing the middle third of a line segment and repeating ad infinitum with the remaining segments.
It is sometimes known as Cantor dust on account of the dust of points that remain after repeatedly removing the middle thirds. (Cantor dust also refers to the multi-dimensional version of the Cantor set.)
The set has some fascinating, counter-intuitive properties:
- It is uncountable. That is, there are as many points left behind as there were to begin with.
- It’s self-similar, meaning each subset looks like the whole set.
- It’s fractal with a dimension that is not an integer.
- It has an infinite number of points but a total length of 0.
Wow!
How To Draw The Cantor Set In Google Sheets
To be clear, the Cantor set is the set of numbers that remain after removing the middle third an infinite number of times. That’s hard to comprehend, let alone do in a Google Sheet 😉
But we can create a picture representation of the Cantor set by repeating the algorithm ten times, as shown in this tutorial:
Create The Data
Step 1:
In a blank sheet called “Data”, type the number “1” into cell A1.
Step 2:
In cell B1, type this formula:
={ FILTER(A1:A,A1:A<>"") ;
SUM(FILTER(A1:A,A1:A<>"")) ;
FILTER(A1:A,A1:A<>"") }Step 3:
Drag this across your sheet up to column J, which creates the data for the first 10 iterations.
Each formula references the column to the left. For example, the formula in cell D will reference column C.
Your data will look like this:
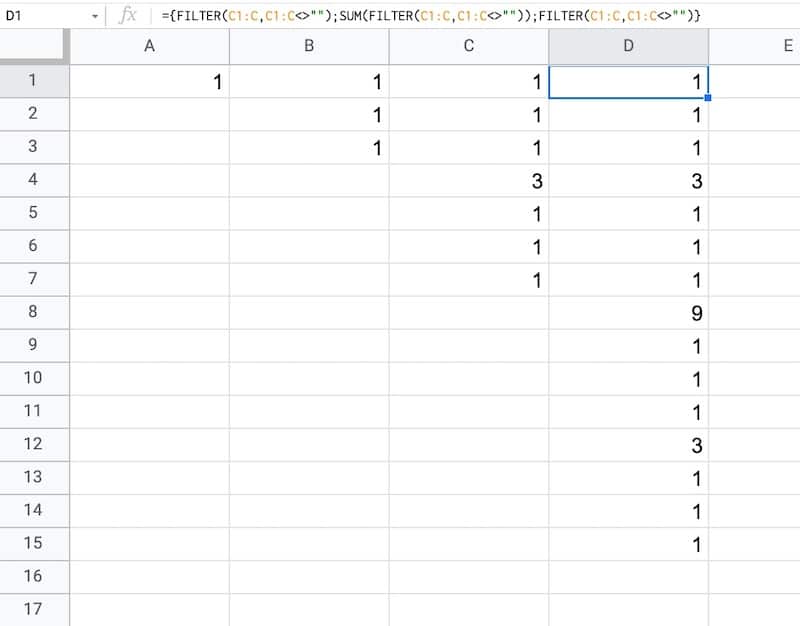
How does this formula work?
It combines array literals and the FILTER function.
Let’s break it down, using the onion framework.
The innermost formula is:
=FILTER(A1:A,A1:A<>"")This formula grabs all the data from column A and returns any non-blank entries, in this case just the value “1”.
Now we combine two of these together with array literals:
={ FILTER(A1:A,A1:A<>"") ;
FILTER(A1:A,A1:A<>"") }Here the array literals { ... ; ... } stack these two ranges.
In this first example, it puts the number “1” with another “1” beneath it in column B.
Then we add a third FILTER and also SUM the middle FILTER range to create our final Cantor set algorithm:
={ FILTER(A1:A,A1:A<>"") ;
SUM(FILTER(A1:A,A1:A<>"")) ;
FILTER(A1:A,A1:A<>"") }As we drag this formula to adjacent columns, the relative column references will change so that it always references the preceding column.
In column B, the output is:
1,1,1
Then in column C, we get:
1,1,1,3,1,1,1
And in column D:
1,1,1,3,1,1,1,9,1,1,1,3,1,1,1
etc.
This data is used to generate the correct gaps for the Cantor set.
Draw The Cantor Set
We’ll use sparklines to draw the Cantor set in Google Sheets.

Step 4:
Create a new blank sheet and call it “Cantor Set”.
Step 5:
Next, create a label in column A to show what iteration we’re on.
Put this formula in cell A1 and copy down the column to row 10:
="Cantor Set "&ROW()This creates a string, e.g. “Cantor Set 1”, where the number is equal to the row number we’re on.
Step 6:
The next step is to dynamically generate the range reference. As we drag our formula down column B, we want this formula to travel across the row in the “Data” tab to get the correct data for this iteration of the Cantor set.
Start by generating the row number for each row with this formula in cell B1 and copy down the column:
=ROW()(I set up my sheet with the data in columns because it’s easier to create and read that way. But then I want the Cantor set in a column too, hence why I need to do this step.)
Step 7:
Use the row number to generate the corresponding column letter with this formula in cell C1 and copy down the column:
=ADDRESS(1,ROW(),4)This uses the ADDRESS function to return the cell reference as a string.
Step 8:
Remove the row number with this formula in cell D1 and copy down the column:
=SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1,ROW(),4),"1","")Step 9:
Combine these two references to create an open-ended range reference for the correct column of data in the “Data” sheet.
Put this formula in cell E1 and copy down the column:
="'Data'!"&ADDRESS(1,ROW(),4)&":"&SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1,ROW(),4),"1","")This returns range references e.g. 'Data'!A1:A
Step 10:
Put this formula in cell F1 and copy down the column:
=INDIRECT("'Data'!"&ADDRESS(1,ROW(),4)&":"&SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1,ROW(),4),"1",""))This will show #REF! errors: “Array result was not expanded because it would overwrite data in…”
However, don’t worry, these are only temporary as we’ll dump this data into the sparkline formula next.
Step 11:
In column G, create a default sparkline formula:
=SPARKLINE(INDIRECT("'Data'!"&ADDRESS(1,ROW(),4)&":"&SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1,ROW(),4),"1","")))This shows the default line chart (except for the first row where it shows a #N/A error).
Step 12:
In column H, convert the line chart sparkline to a bar chart sparkline by specifying the charttype in custom options:
=SPARKLINE(INDIRECT("'Data'!"&ADDRESS(1,ROW(),4)&":"&SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1,ROW(),4),"1","")),{"charttype","bar"})Step 13 (optional):
Finally, in column I, change the colors to a simple black and white scheme, by specifying color1 and color2 inside the sparkline:
=SPARKLINE(INDIRECT("'Data'!"&ADDRESS(1,ROW(),4)&":"&SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1,ROW(),4),"1","")),{"charttype","bar";"color1","black";"color2","white"})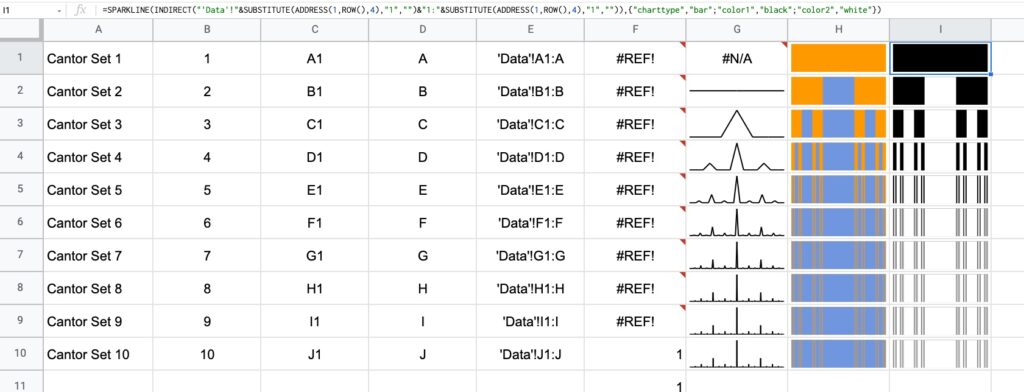
Feel free to delete any working columns once you have finished the formula showing the Cantor set.
Finished Cantor Set In Google Sheets
Here are the first 10 iterations of the algorithm to create the Cantor set:

Of course, this is a simplified representation of the Cantor set. It’s impossible to create the actual set in a Google Sheet since we can’t perform an infinite number of iterations.
Can I see an example worksheet?
See Also
You might enjoy my other mathematical Google Sheet posts:
PI Function in Google Sheets And Other Fun π Facts
Complex Numbers In Google Sheets
How To Draw The MandelBrot Set In Google Sheets, Using Only Formulas
The FACT Function in Google Sheets (And Why A Shuffled Deck of Cards Is Unique)
How To Draw The Sierpiński Triangle In Google Sheets
Exploring Population Growth And Chaos Theory With The Logistic Map, In Google Sheets